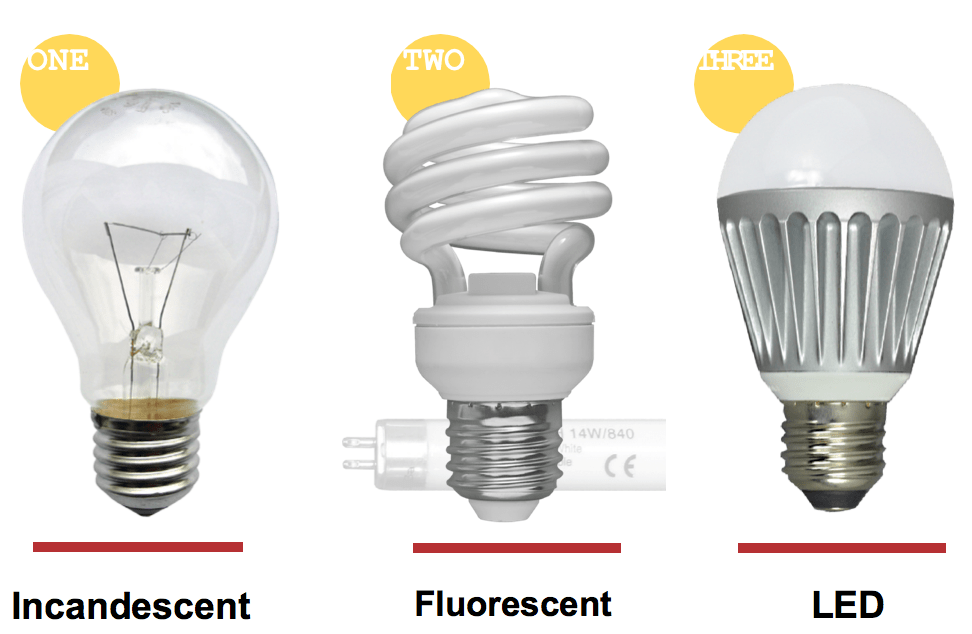
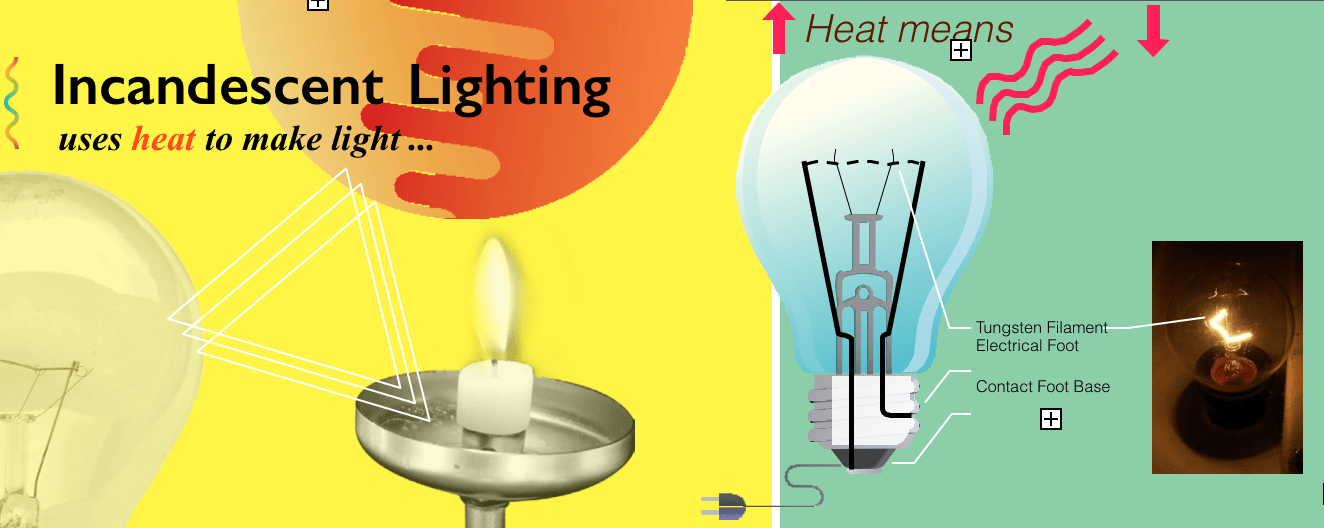
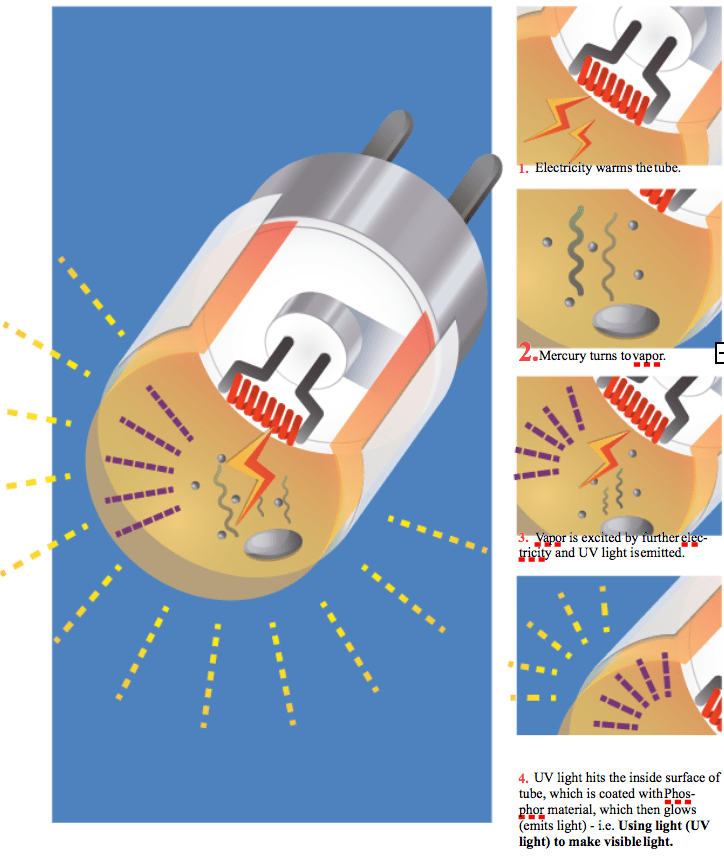
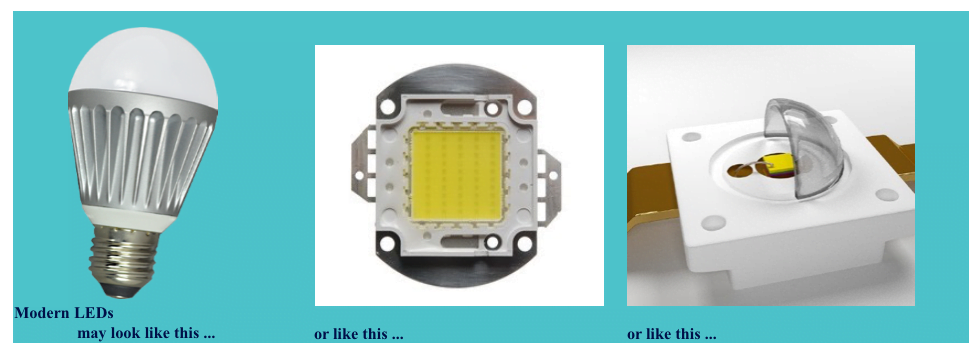
Incandescence
uses heat (thermal radiation) to produce light. Sunlight and Candle-light are generated in this way. Incandescent Light Bulbs also generate heat (ther- mal radiation) through a “fila- ment”-thefilamentheatsupto
produce light like a candle.
The great advantage is that this type of light quality and color is generally very consistent between most brands. Its color qualities are also very close what the Sun produces.
This type of bulb requires lots of energy which is wasted as dissipated heat (90%). Also, the intense heat causes faster degradation of the filament leading to a shorter lifespan of the bulb.
The great disadvantage is that Halogen lights are a type of Incandescent Light but contain Halogen gas inside the bulb to slow down degradation of the filament, allowing it to withstand more heat, and making it suitable for high intensity lights (e.g. car headlights).